There are various types of video adapters, and VGA, DVI, HDMI, DP are the most popular. What are the differences between these four modes? Let us take a closer to find out the truth.
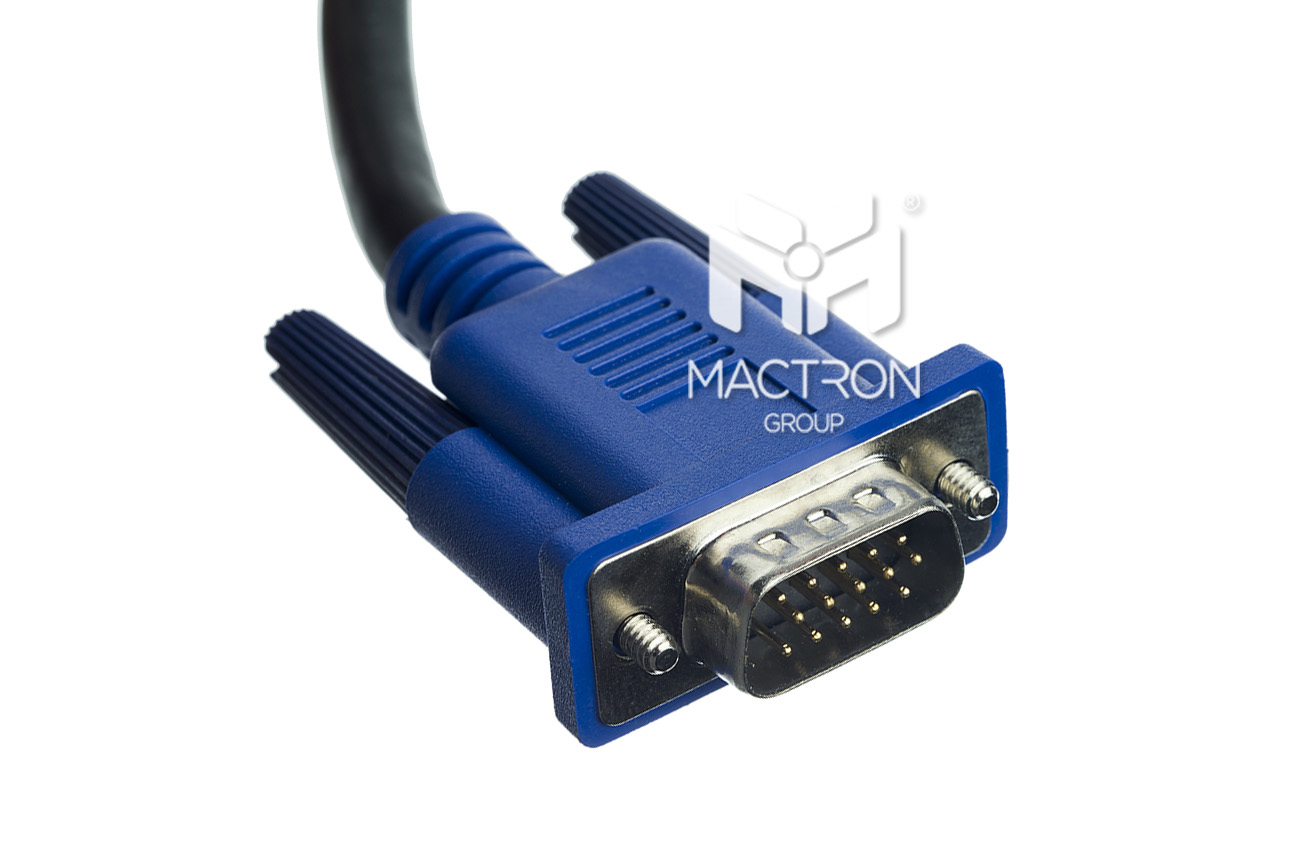
Veteran Screen Mode: VGA
Released: 1987
Also known as D-sub connector, VGA is composed of 15 pins, which is transmitted in the form of analog, which mainly divides the display signal into different types of signals and sends them to the display.
Limitations and Disadvantages of VGA
Generally, VGA may not be able to display images normally if it is more than 15 meters away, and the resolution support can only reach 1920×1080 @ 60 Hz. In addition, since VGA transmits analog, an additional DAC bit is required on the display card The signal is converted to analog, but the analog cannot preserve the color information of each pixel, so the picture quality is poor, especially on larger screens.
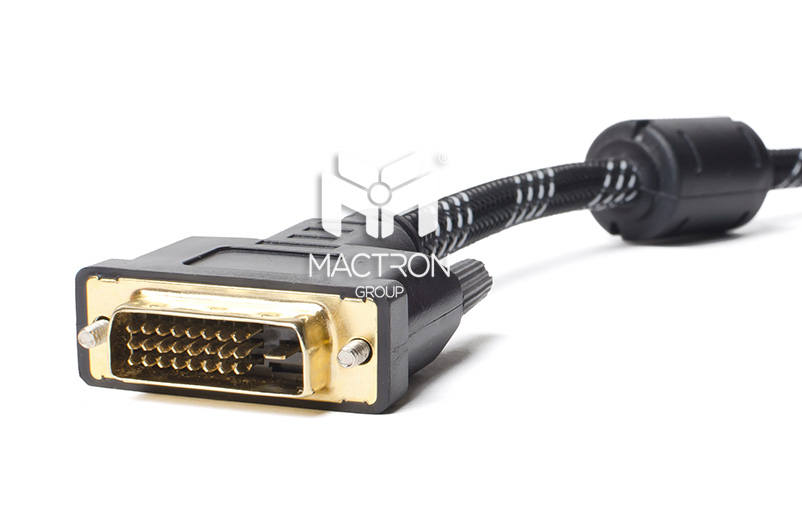
Entering the Digital Age: DVI
Released: 1999
VGA transmits analog signals, the reason is to match the CRT screen, but things have changed drastically after entering the era of LCD monitors. If you want to use VGA interface with LCD screen, you need to go through several signal conversions in the middle, so DVI was born.
Types of DVI
DVI may be the most complicated type among all video adapters. It is mainly divided into three categories and five different connector types. Among them, the three categories are DVI-D, which is fully digital, and DVI-A, which maintains analog signal compatibility. And DVI-I combines the characteristics of both.
Limitations and Disadvantages of DVI
The highest resolution of DVI in Single Link is 1920×1200 @ 60 Hz, and the highest resolution of Dual Link is 2560×1600 @ 60 Hz, which is only a little higher than 2K resolution. Moreover, the size of the DVI connector is too large. Generally, the display card can only accommodate two DVI connectors at most, which brings big trouble to the development of the display.
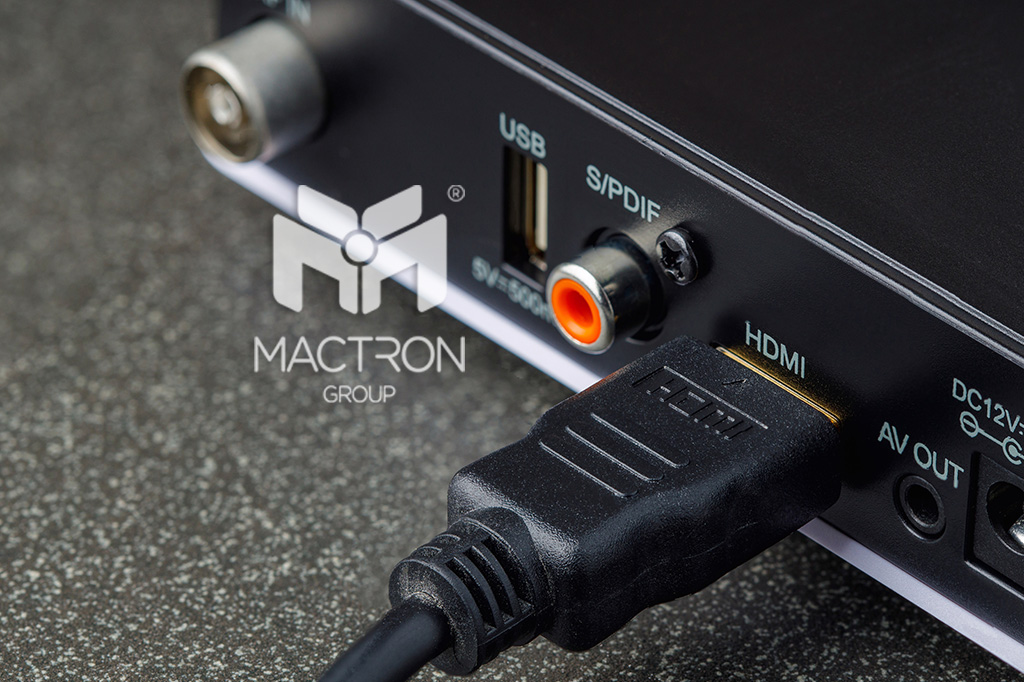
Universal Digitalization: HDMI
Released: 2003
What is special about HDMI is that in addition to video signals, HDMI can also transmit audio signals. After HDMI 1.3 version, it adds support for DTS-HD and Dolby TrueHD.
Types of HDMI
HDMI can be divided into five different connector types, namely Type A to E. Type A, C, and D are only different in size, the transmitted content is consistent, so they can be converted to each other. Type B is the Type A corresponding to the DVI Dual Link version. It is very similar to Type A in appearance but wider. Type E is the version for automotive electronics.
Limitations and Disadvantages of HDMI
The most criticized thing about HDMI is that there are a bunch of versions, even the transmission lines are distinguished. The previous version was not much different. The difference is obvious after version 1.3. 1.4 supports 3D images and 1080 resolution at 120 Hz. The 2.0 version can stably support 4K resolution 60 Hz.
HDMI cable identification
The cable with this mark belongs to the HDMI 1.4 standard version, which cannot support 1080p resolution and can only support up to 1080i resolution.
The cable with this mark belongs to HDMI 1.4 high-speed version, which can support 1080p and 2K, 4 resolution and 3D picture.
This kind of mark only appears on the HDMI 2.0 cable, which can support up to 4K @ 60 Hz images. This type of cable must be tested by the HDMI organization and will be issued after passing the test. Due to additional certification fees, such cables are particularly expensive.
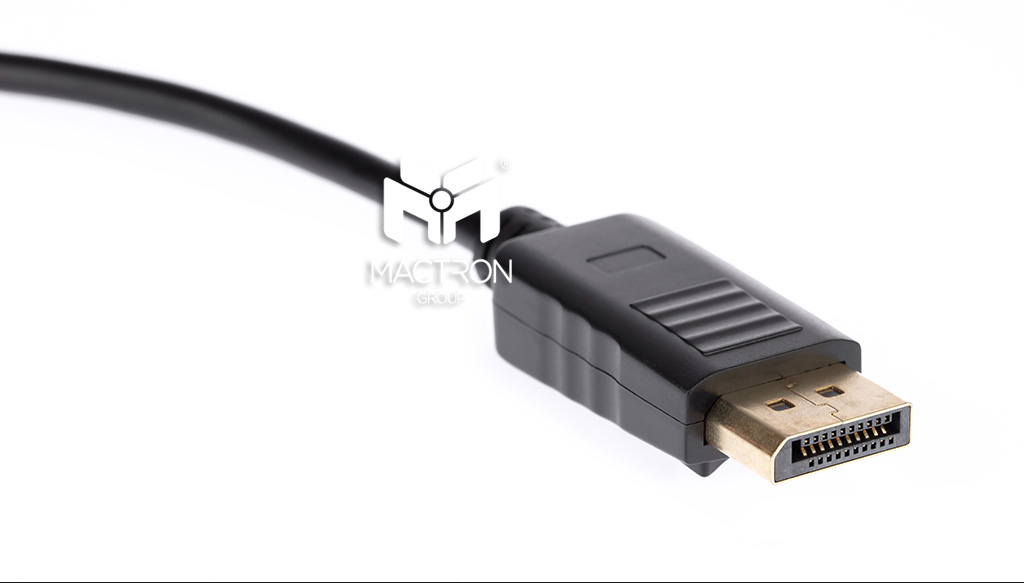
The DVI's Successor: DisplayPort
Released: 2006
DisplayPort is a relatively new specification. Overall, its characteristics are similar to HDMI. However, DisplayPort abandons the TMDS technology used in DVI and HDMI in the past and uses LVDS instead. It uses a packet technology similar to Ethernet to transmit data.
The benefit of using the packet method is that DisplayPort can achieve the function of a single interface corresponding to several independent devices through a hub, which makes a breakthrough in the development of multi-screen architecture.
Limitations and Disadvantages of DisplayPort
The initial 1.0 version can support a transmission rate of 8.64 Gbps, but the limitation is that the transmission line is only up to 2 meters long.
The new 1.3 and 1.4 versions can support a maximum resolution of 4K or even 8K, but the 8K resolution with a 60 Hz update frequency requires version 1.4 with Display Stream Compression technology to achieve.
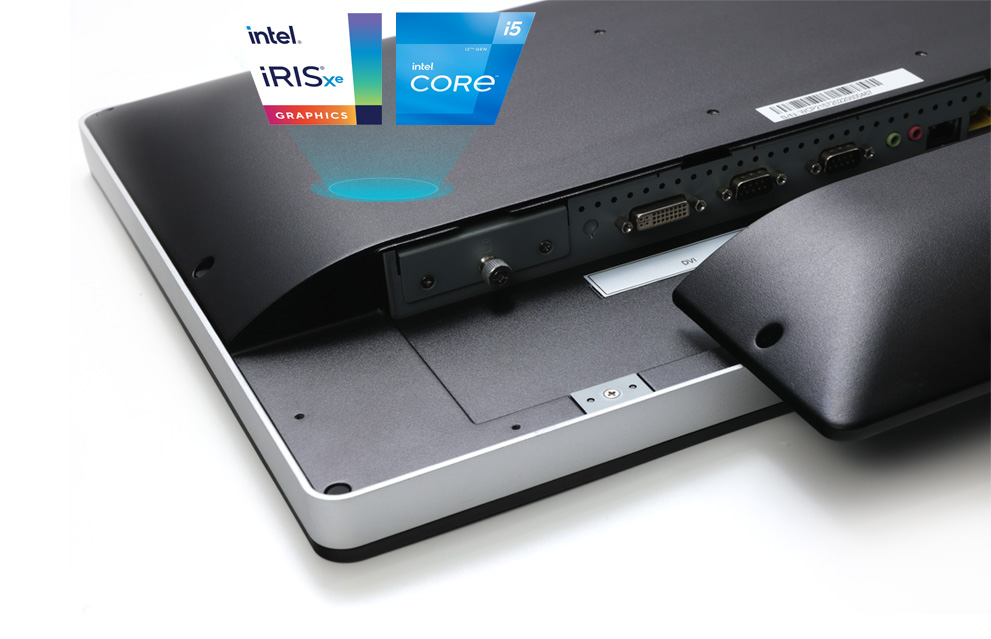
What We Use on the WCP & WMP Series?
Our WCP/WMP series uses HDMI 2.0 that can support 4K / 60 Hz and DVI-I mode which supports 2560×1600 / 60 Hz, and this year we also upgraded the CPU to the Intel 12th generation. Such specifications must not be missed.
Check out MACTRON GROUP(MTG)’s new WCP Series and WMP Series. Our WCP Series will replace the processor from 8th Gen to 12th Gen early next year, which can perfectly fit all the specification upgrades of the 12th Gen processor. Take a look at this series, maybe there will be unexpected gains for you.