Warehouse management has always been a critical link in the logistics chain, directly impacting the storage, transportation, and distribution of goods. However, with the rapid advancement of technology, we are witnessing a revolution in the field of warehouse management, where volume measurement and ToF (Time of Flight) technology play a crucial role, bringing new possibilities to warehouse management.
Volume Measurement: Insights Beyond Surface
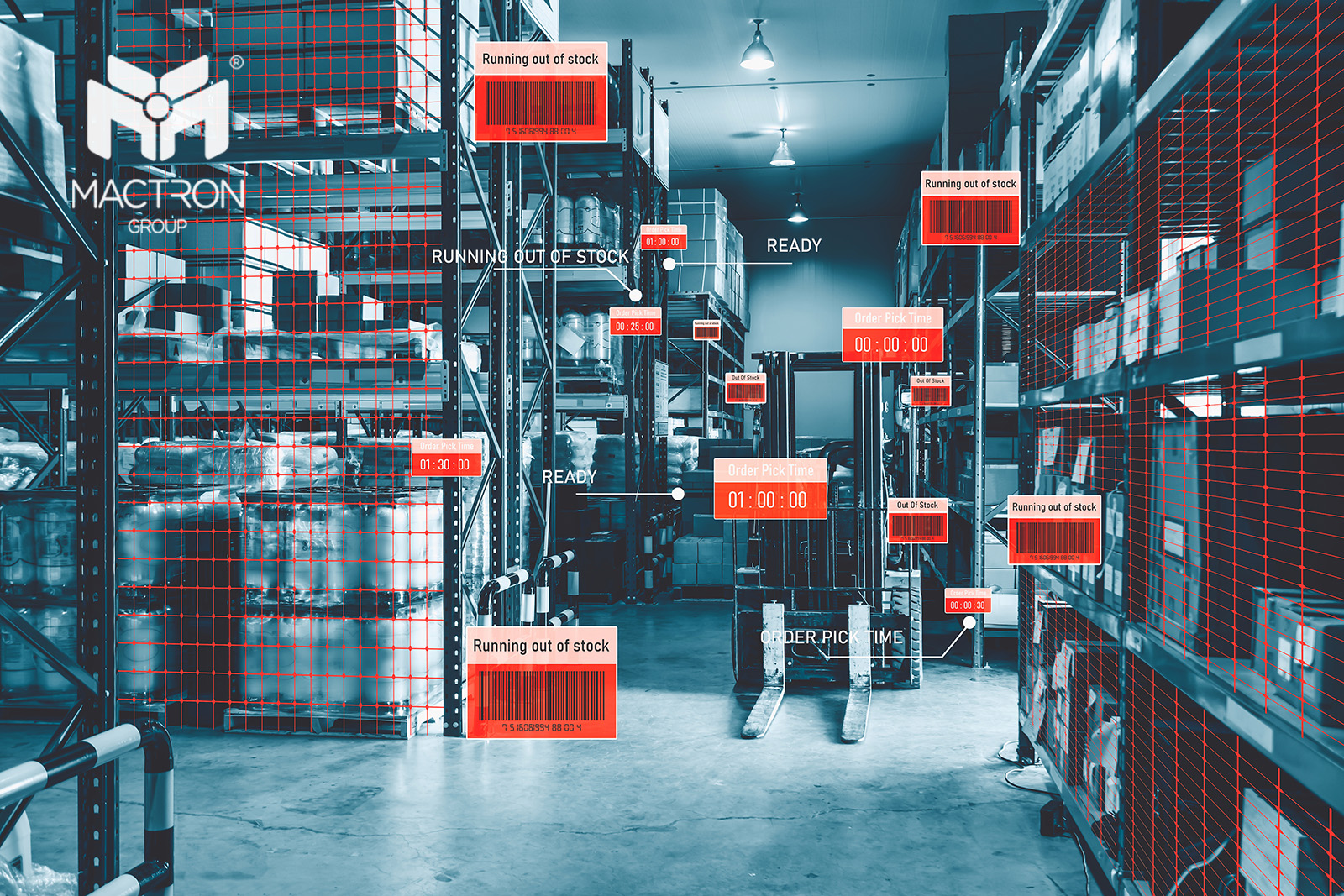
In traditional warehouse management, the volume of items is often handled with estimated or approximate values, which can lead to wastage of storage space and decreased transportation efficiency. However, through volume measurement technology, we are able to gain a deeper understanding of the actual volume of each item, enabling more precise storage and layout arrangements to optimize the utilization of warehouse space.
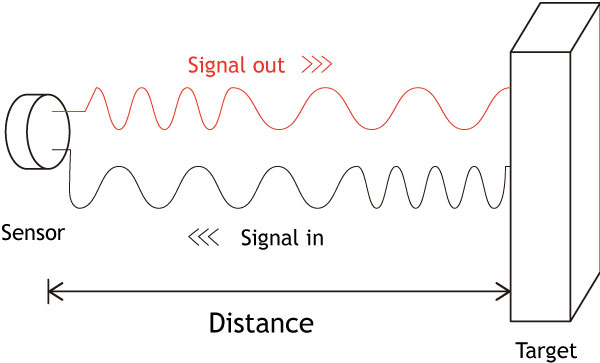
ToF Principle: The Technological Ally of Warehouse
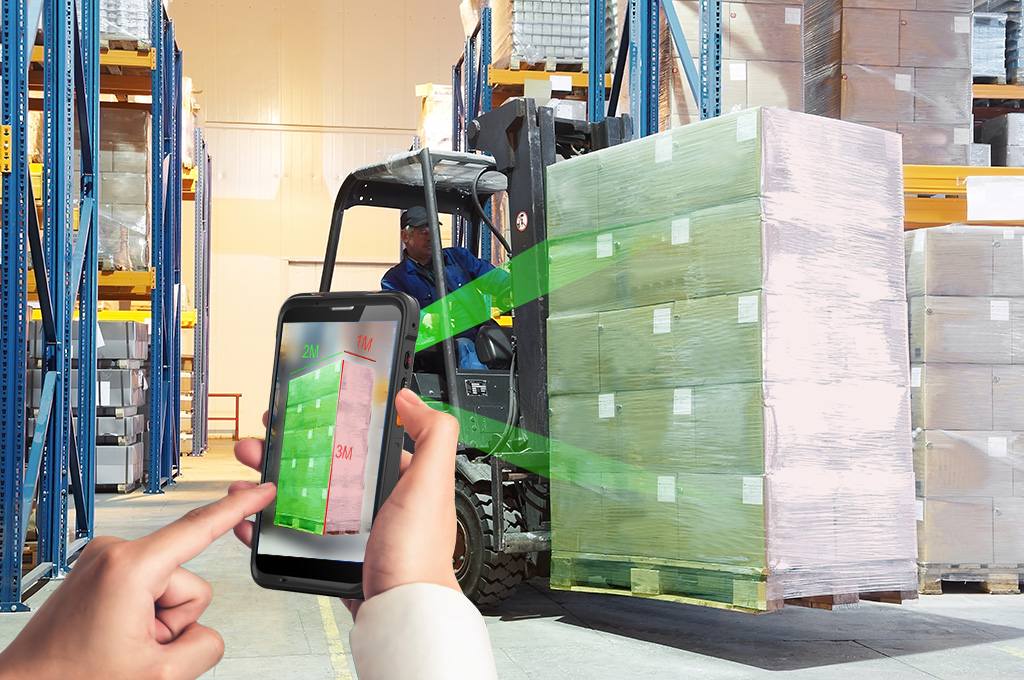
ToF technology is becoming a powerful ally in warehouse management. It measures the distance of objects based on the speed of light propagation, enabling rapid and accurate measurements of items for precise warehouse management. Specifically, ToF technology helps us quickly determine the volume of each item, optimizing storage, transportation, and distribution processes.
Applications of ToF Technology in Warehouse Management
Goods Storage:
Using ToF technology, warehouse managers can quickly measure the volume of each item, determining the optimal storage location and stacking method for maximizing space utilization.
Transportation Optimization:
During the transportation process, ToF technology can help determine the efficient utilization of transport containers, reducing space wastage and enhancing transportation efficiency.
Inventory Management:
Regularly measuring the volume of individual items in inventory, warehouse managers can achieve more accurate inventory management, minimizing situations of excess or insufficient stock.
Future Prospects: Technology Empowering the Future of Warehousing
Volume measurement is sparking a revolution in the field of warehouse management and reshaping our perspective on it. The application of this technology will bring more efficient and precise management methods to warehouse operations, simultaneously reducing costs and enhancing customer satisfaction. We can expect the field of warehouse management to become increasingly intelligent and efficient, presenting more opportunities and challenges for the future of the logistics industry.
MCA0556 without Volume Measurement Module (left) and with Volume Measurement Module (right).
Check out
MACTRON GROUP(MTG)’s
MCA Series. The
MCA0556 in our Commercial Grade Android Mobile Tablet PC can be equipped with Volume Measurement, which can detect the goods in 40CM to 4M, and the error is less than 5%, which can definitely satisfy all your imagination for this application.